 |
|||
|
Page Title:
Figure 11-8.--Stray-current corrosion. |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|
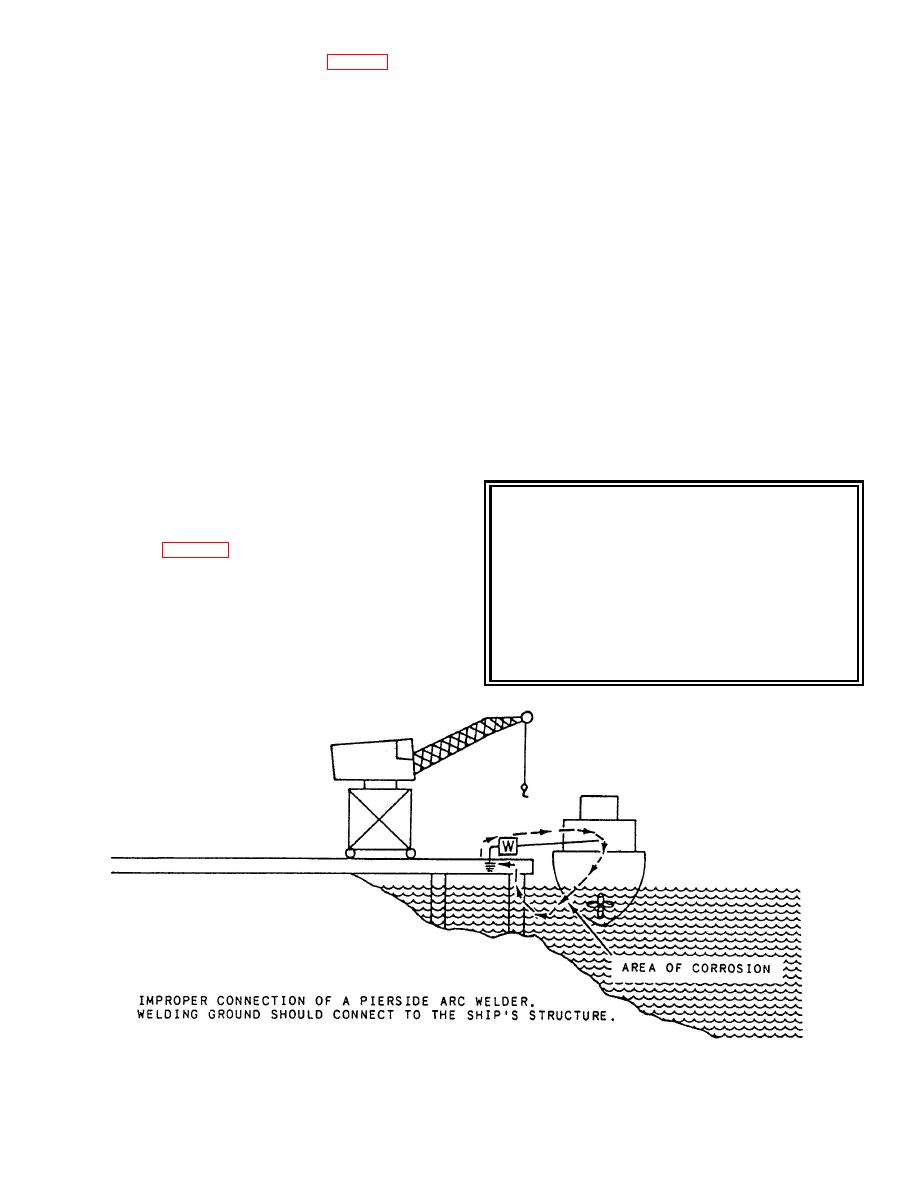 welding machine is not correctly made (fig. 11-8) or no
TYPES OF SACRIFICIAL ANODES.-- The
return lead to the welder is connected, you could have
following is a list of sacrificial anodes:
current flow between the ship's hull and the pier,
Zinc
causing corrosion to form on the hull.
Aluminum
Seawater resistivity is the concentration of ions
Magnesium
in seawater, which acts as a resistance to current flow
between two dissimilar metals. Normal seawater gener-
Iron
ally has a nominal resistivity of 20 to 22 ohms/cm at a
Steel waster pieces
temperature of 20C (68F). In brackish or fresh water
this resistivity may vary.
Zinc Anodes.-- Zinc anodes are used for anodic
polarization on steel or aluminum surfaces. They have a
TYPES OF CATHODIC PROTECTION
half-cell potential of a negative 1.04 volts. They can be
either bolted or welded to the hull. Welding is the
There are two types of cathodic protection
preferred method because the anodes will have a secure
systems, the sacrificial anode and the impressed current.
electrical and mechanical attachment.
Each system will be addressed separately.
Aluminum Anodes.-- Aluminum anodes are
Sacrificial Anode System
currently being tested and evaluated by the Naval Sea
Systems Command (NAVSEA). The use of aluminum
The sacrificial anode system is based on the
anodes requires prior NAVSEA authorization and
principle that a more reactive metal, when installed
design review. It is also necessary to obtain guidance
near a less reactive metal and submerged in an
from NAVSEA before preparing a cathodic protection
electrolyte such as seawater, will generate a potential of
system design using aluminum anodes.
a sufficient magnitude to protect the less reactive metal.
In this process, the more reactive metal is sacrificed.
CAUTION
Sacrificial anodes attached to a ship's hull slowly oxidize
Do not use magnesium anodes on
and generate a current (see the electrochemical
aluminum hulls. Production of an
corrosion cell in fig. 11-6 that protects the hull and its
alkaline (basic corrosion product) may
appendages). This system does not have an onboard
lead to serious corrosion of the
control of protecting current, and depends on the limited
aluminum metal structure. Aluminum is
current output of the anode. This type of system
referred to as an amphoteric material
requires anode replacement on a fixed schedule (usually
because it is subject to deterioration by
every 3 years on naval ships). The system is rugged and
simple, requires little or no maintenance, and always
both
acid
and
basic
solutions.
protects the ship.
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |