 |
|||
|
Page Title:
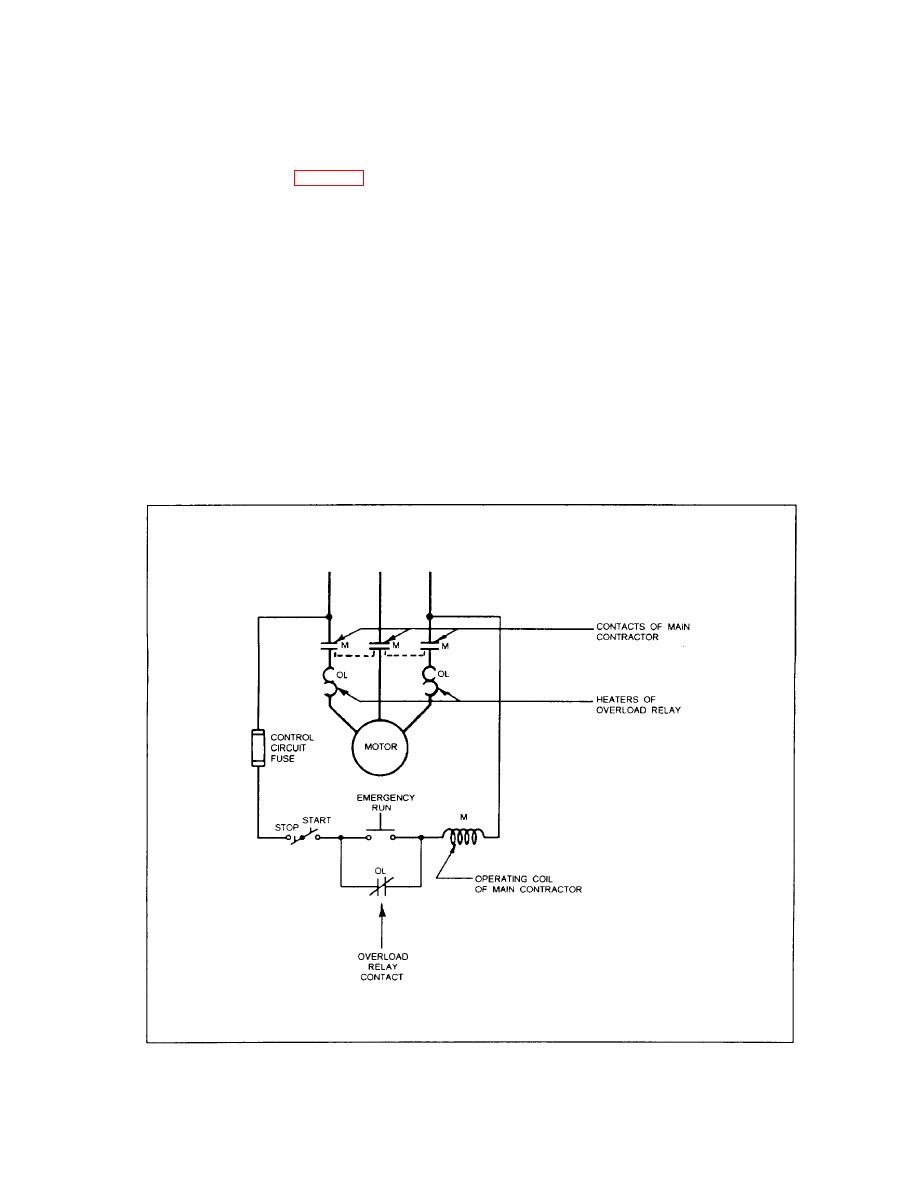
Figure 2-40.-Schematic diagram of motor controller with thermal type of overload relay. |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|
 the relay. After the relay trips, the solder cools and
mechanism releases. The heater coils are rated so that
solidifies, and the relay is ready to be reset.
normal circuit current will not produce enough heat to
release the ratchet mechanism.
BIMETAL TYPE.-- The heat-sensitive element
is a strip or coil of two different metals fused together
The thermal type of overload relay has a heat-
along one side. When heated, one metal expands more
sensitive element and an overload heater connected in
than the other, causing the strip or coil to bend or
series with the motor circuit (fig. 2-40). When the
deflect and open the overload relay contacts.
motor current is excessive, heat from the heater causes
SINGLE-METAL TYPE.-- The heat-sensitive
the heat-sensitive element to open the overload relay
element is a metal tube around the heater. The tube
contacts. As it takes time for the heat-sensitive
lengthens when heated and opens the overload relay
element to heat up, the thermal type of overload relay
contacts.
has an inherent time delay. Thermal overload relays
INDUCTION TYPE.-- The heat-sensitive
may be of the solder-pot, bimetal, single-metal, or
element is usually a bimetal strip or coil. The heater
induction type.
consists of a coil in the motor circuit and a copper tube
SOLDER-POT TYPE.-- The heat-sensitive
inside the coil. The copper tube acts as a short-
element is a solder pot that consists of a cylinder inside
circuited secondary of a transformer and is heated by
a hollow tube. These are normally held together by a
the current induced in it. This type of overload relay
film of solder. In case of excessive motor current, the
is used only in ac controllers, whereas the previously
described types of thermal overload relays may be
heater melts the solder, breaks the bond between the
used in ac or dc controllers.
tube and cylinder, and releases the tripping device of
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |