 |
|||
|
Page Title:
Figure 4-5.--Continuous precession. |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|
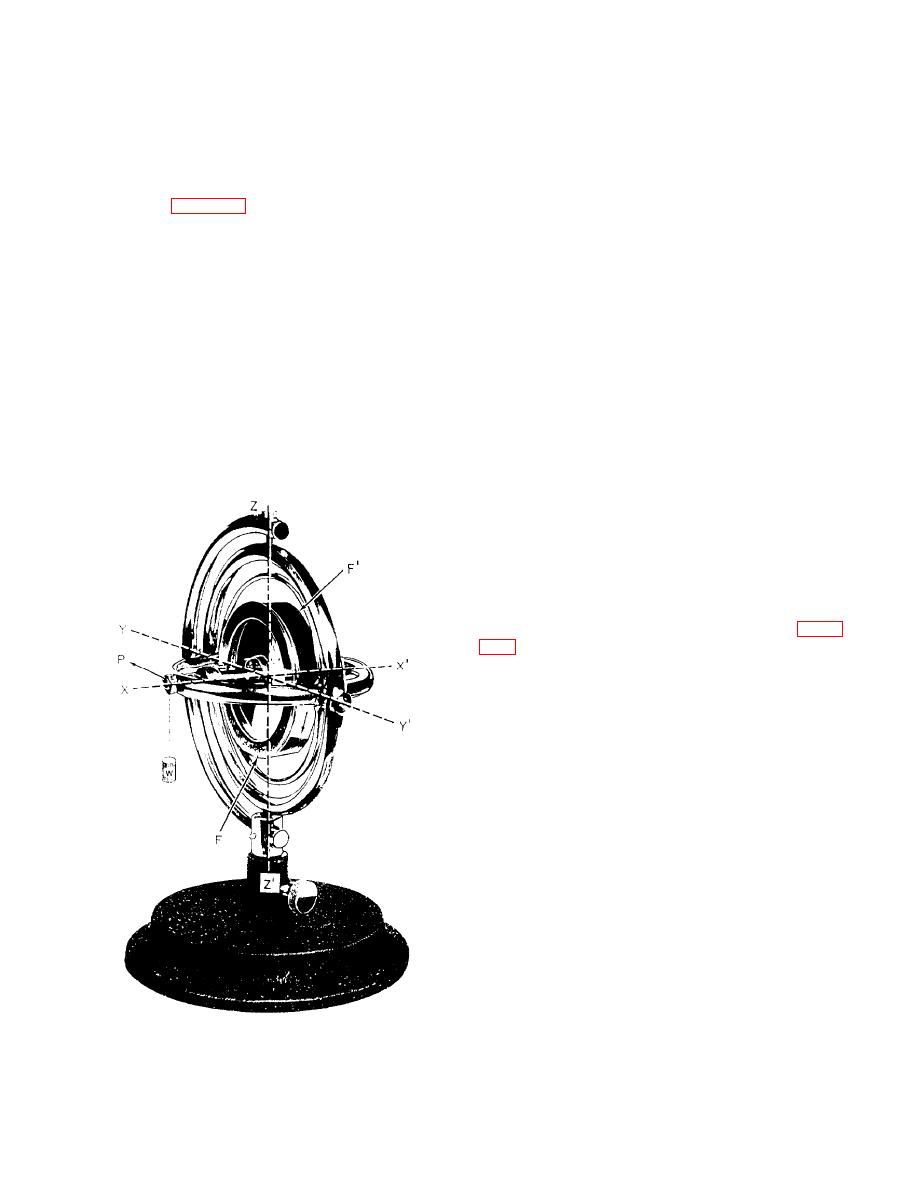 right and continue turning until the weight is re-
gyroscope precesses until it is in the plane of the
moved.
force. When this position is reached, the force is
about the spinning axis and can cause no further
FORCE OF TRANSLATION
precession.
If the plane in which the force acts moves at the
Any force operating through the center of gravity of
same rate and in the same direction as the precession it
the gyroscope does not change the angle of the plane of
rotation but moves the gyroscope as a unit without
causes, the precession will be continuous. This is
changing its position in space. Such a force operating
illustrated by figure 4-5, in which the force attempting
through the center of gravity is known as a force of
to change the plane of rotation is provided by a weight,
translation. Thus, the spinning gyroscope may be moved
W, suspended from the end of the spin axle, X. Although
freely in space by means of its supporting frame, or case,
the weight is exerting a downward force, the torque is
without disturbing the plane of rotation of the rotor. This
felt 90 away in the direction of rotation. If the wheel
condition exists because the force that is applied through
rotates clockwise, as seen from the weighted end,
the supporting frame acts through the center of gravity
precession will occur in the direction of arrow P. As the
of the rotor and is a force of translation. It produces no
torque on the gyro rotor.
gyroscope precesses, it carries the weight around with
it so that forces F and F1 continuously act at right angles
EFFECT OF EARTH'S
to the plane of rotation, and precession continues
ROTATION
indefinitely. In other words, the rotor will turn to the
As just explained, a free-spinning gyroscope
can be moved in any direction without altering the
angle of its plane of rotation. If this free-spinning
gyroscope is placed on the earth'is surface at the equator,
with its spinning axis horizontal and aligned east and
west, an observer in space below the South Pole would
note that the earth rotates clockwise from west to east
and carries the gyroscope along. As the earth rotates,
rigidity of plane keeps the gyroscope wheel fixed in
space and rotating in the same plane at all times. Figure
that the gyroscope is set spinning at 0000 hours
with its spinning axis aligned east and west and
parallel to the earth's surface. At 0600, 6 hours after the
gyroscope was started, the earth has rotated 90 and
the axle of the gyroscope is aligned with the original
starting position. At 1200 the earth has rotated 180,
while the gyroscope returns to its original position. The
figure shows how the gyro completes a full cycle in a
24-hour period.
APPARENT ROTATION OF THE
GYROSCOPE
An observer on the earth's surface does not see
the operation of the gyro in the same way as an
observer in space does. On the earth, the gyro
appears to rotate, while the earth appears to stand
still. As the earth rotates, the observer moves with
it, so the gyroscope seems to rotate around its
horizontal axis. The effect the observer sees on the
earth is called apparent rotation and also is referred
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |